Tapped Inductor Boost
Description of the Tapped Inductor Boost converter component in Schematic Editor
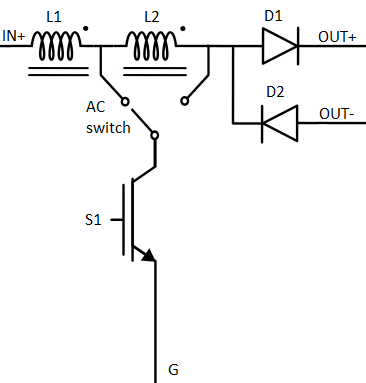
Schematic Block Diagram
A schematic block diagram of the Tapped Inductor Boost switching block is given in Figure 1.
Weight of a Tapped Inductor Boost component for real-time simulation is 1.
Control
Selecting Digital inputs as the Control parameter enables assigning gate drive inputs to any of the digital input pins (from 1 to 32(64)). For example, if S1 is assigned to 1, the digital input pin 1 will be routed to the S1 switch gate drive. In addition, the gate_logic parameter selects either active high (High-level input voltage VIH turns on the switch), or active low (Low-level input voltage VIL turns on the switch) gate drive logic, depending on the design of the external controller. In TyphoonSim, digital signals are read from the internal virtual IO bus. Hence, if some signal is sent to digital ouput 1, it will appear on digital input 1.
Selecting Internal modulator as the Control parameter, enables use of the internal PWM modulator for driving S1 and AC switch switches instead of digital input pins. In this configuration, three additional component inputs will be present. En input is used as enable/disable and In and In1 are used as referent signal inputs for internal PWM modulator.
Selecting Model as the Control parameter, enables setting of the IGBTs gate drive signals directly from the signal processing model. The input pin gates appears on the component. It is a vector input of 2 gate drive signals in the following order: [S1, AC switch]. When controlled from the model, logic is always active high.
Digital Alias
If a converter is controlled by digital inputs, an alias for every digital input used by the converter will be created. Digital input aliases will be available under the Digital inputs list alongside existing Digital input signals. The alias will be shown as Converter_name.Switch_name, where Converter_name is name of the converter component and Switch_name is name of the controllable switch in the converter.
Ports
- IN+ (electrical)
- DC input + port
- G (electrical)
- G port
- OUT+ (electrical)
- DC output + port
- OUT- (electrical)
- DC output - port
- gates (in)
- Available if model control is selected
- 1-element (scalar) input gate signal for switch
- En (in)
- Available if Internal modulator control is selected
- Used to enable/disable internal modulator
- In (in)
- Available if Internal modulator control is selected
- Used to specify modulation signal value for internal modulator
- In1 (in)
- Available if Internal modulator control is selected
- Used to specify modulation signal value for internal modulator
- Freq (in)
- Available if Internal modulator control is selected and Variable carrier frequency is selected as the modulator's operation mode
- Used to specify modulator's carrier frequency
General (Tab)
- Control
- Specifies how switches are controled. It is possible to choose between: Digital inputs, Internal modulator, and Model
- More details about each type of control can be found in the Control section
- If Digital inputs is selected as Control, the following
properties can be used:
- S1
- Digital input that is used to control S1 switch
- S1_logic
- Logic that will be applied to control signal for S1
- Active high or active low
- AC switch
- Digital input that is used to control AC switch
- AC_switch_logic
- Logic that will be applied to control signal for AC switch
- Active high or active low
- Gate control enabling
- If enabled, gives a possibility to control if changes in the gate control signal are applied or not
- Sen
- Available if Gate control enabling is enabled
- Digital input that enables/disables switching
- Sen_logic
- Available if Gate control enabling is enabled
- Logic that will be applied to Sen signal
- S1
- If Model is selected as Control, the following properties can
be used:
- Execution rate
- Defines the period between two updates of gate signals for the component. Gate signals are provided as a signal processing input to component
- Execution rate
- If Internal modulator is selected as Control, the following
properties can be used:
- Operation mode
- Specifies the source of the internal modulator carrier frequency
- If Operation mode is Fixed carrier frequency, then frequency can be specified on the component properties
- If Operation mode is Variable carrier frequency, then the frequency can be specified using a signal processing port
- Carrier frequency (Hz)
- Available if the Operation mode is a Fixed carrier frequency
- Specifies the internal modulator's carrier frequency
- Carrier phase offset
- Specifies the internal modulator's carrier phase offset in degrees
- Dead time period
- Specifies dead time for the internal modulator in seconds
- Reference signal [min, max]
- Specifies carrier signal minimal and maximal value
- Vector containing two values: the minimal carrier signal value, followed by the maximal carrier signal value
- Load mode
- Specifies on which event the new value of the modulation signal will be
applied in the internal modulator
- If on min is selected, new value will be applied when carrier reaches minimal value
- If on max is selected, new value will be applied when carrier reaches maximal value
- If on either is selected, new value will be applied when carrier reaches minimal or maximal value
- Specifies on which event the new value of the modulation signal will be
applied in the internal modulator
- Operation mode
Electrical (Tab)
- Coupling coefficient
- Represents coupling element between the inductors L1 and L2
- Value must be between 0.95 and 1
- L1
- Specifies inductance value for L1 inductor
- L2
- Specifies inductance value for L2 inductor
- R1
- Specifies resistance value for R1 resistor
- R2
- Specifies resistance value for R2 resistor
Extras (Tab)
- Public - Components marked as public expose their signals on all levels.
- Protected - Components marked as protected will hide their signals to components outside of their first locked parent component.
- Inherit - Components marked as inherit will take the nearest parent 'signal_access' property value that is set to a value other than inherit.