Introduction
In electric vehicles (EVs), the battery management system (BMS) plays an essential role in ensuring the efficient operation and safety of the battery. Its key operations include managing battery life cycles, estimating the state of charge (SoC), monitoring the state of health (SoH), cell balancing, and fault detection.
Given the increasing demands of EV applications and batteries, validating BMS under real-world conditions is critical for ensuring reliability, safety, and performance. Faulty BMS operation can result in degraded battery lifespan, inefficient energy utilization, or severe failures, emphasizing the importance of rigorous testing.
Overcoming Challenges in BMS Development
Developing an efficient BMS presents significant challenges due to the complexity of battery system dynamics. Balancing issues arise from non-linear, temperature-dependent battery behavior, coupled with pack-cell variations. Inefficient thermal stability and fault detection can result in severe consequences, including thermal runaway.
Another challenge is the need to test various battery chemical compositions and accurately model their unique dynamics under different BMS operating scenarios. Additionally, engineers face the dual pressures of reducing development timelines while adhering to stringent safety and performance standards.
Real-Time Validation with Typhoon HIL’s BMS HIL Testbed
To address these challenges, we’ve developed the BMS HIL Testbed. Built on a modular, scalable solution, the BMS HIL Testbed empowers engineers to simulate, test, and refine BMS strategies in a risk-free environment. The cutting-edge BMS testing solution is comprised of:
Real-Time Simulator | High-Fidelity Simulation
A real-time simulator delivers precision when modeling battery systems’ electrical and thermal dynamics. This high-fidelity simulator replicates diverse operating conditions and faults, ensuring robust validation of BMS algorithms. Engineers can accurately evaluate performance metrics, optimize SoC estimation, and test fail-safes without the risks associated with physical batteries. In Figure 1, see HIL606, the Typhoon HIL flagship real-time simulator.

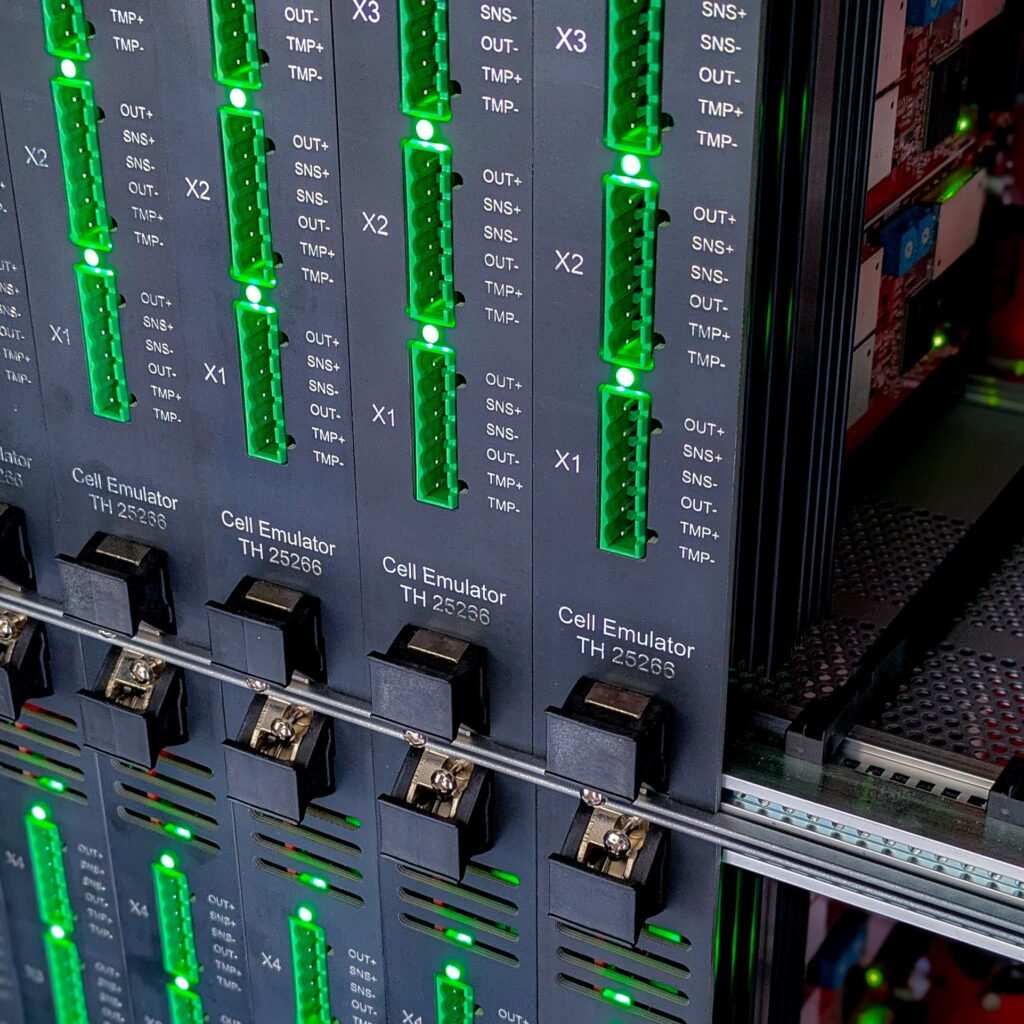
Smart Cell Emulator | Mastering Battery Cell-Level Complexity
The non-linear, temperature-dependent behavior of batteries, combined with variations in capacity and internal resistance, makes accurate estimations of SoC and SoH a significant challenge. The Smart Cell Emulator (see Fig. 2) addresses this by precisely emulating individual cell behavior, delivering ±0.05% FS accuracy in voltage measurements (±8V output with < ±0.5mV ±0.05% FS accuracy) and current measurements (±1A high range, accuracy < ±0.2mA ±0.05% FS; ±10mA low range, accuracy < ±5μA ±0.05% FS). These capabilities enable accurate SoC and SoH estimation under varying conditions, helping refine battery health monitoring algorithms.
Balancing battery cells is equally complex due to differences in capacity and resistance, which can impact overall pack performance and lifespan. The Smart Cell Emulator provides precise control over individual cell parameters, including capacity, internal resistance, and temperature. With up to 256 cell emulation channels and channel isolation up to 1kV, it supports detailed testing and refinement of cell-balancing algorithms to maintain uniform charge and discharge cycles across battery packs.
To enhance thermal stability, the emulator features thermistor emulation with 10kΩ NTC and 10Ω resolution and ±0.5°C ±0.25% FS accuracy, enabling precise thermal testing and monitoring. Additionally, its fault insertion capabilities, including open circuit, short circuit, and reverse polarity, allow for a thorough evaluation of BMS fault responses under real-world conditions while maintaining safety.
Typhoon HIL’s solution supports multiple battery chemistries and features a scalable architecture capable of accommodating systems ranging from 60V to 800V. This flexibility enables testing BMS designs for a variety of applications, including EVs, ensuring compatibility and high performance across different battery chemistries.
Reducing BMS development timelines without compromising safety and performance is critical. The Smart Cell Emulator streamlines the process by accurately replicating lifecycle effects, capacity variations, and real-world fault conditions, minimizing dependence on physical batteries in the lab. This accelerates the testing cycle while upholding high safety standards, facilitating faster time-to-market for robust and reliable BMS solutions.

HIL SCADA | Real-Time Monitoring and Control
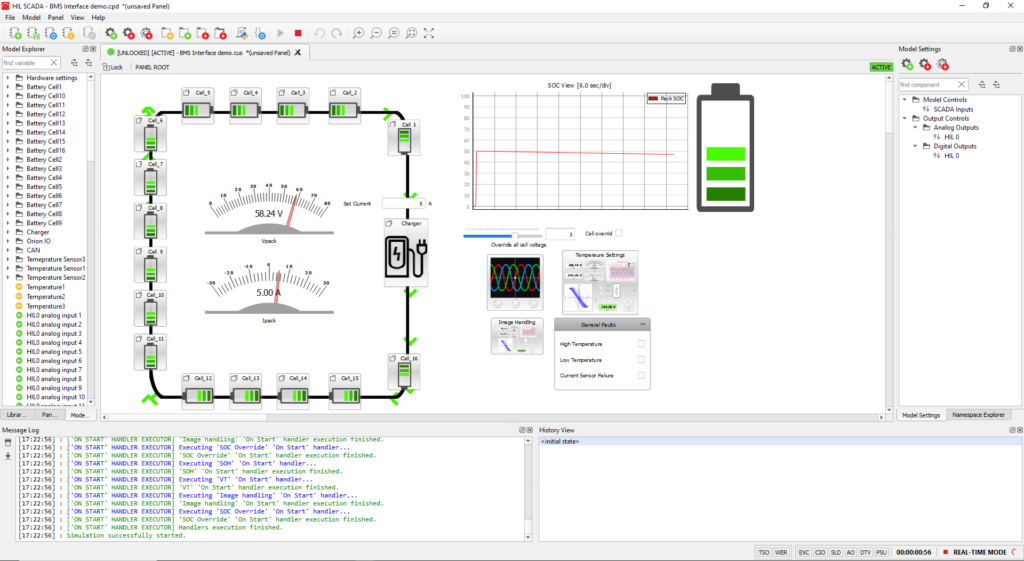
The user-friendly HIL SCADA interface (see Fig. 3) provides seamless monitoring and control of simulated environments. With this tool, you can visualize critical parameters—such as voltage, current, temperature, and SoC in real time during BMS testing. Real-time data visualization and parameter tuning offer detailed insights into system behavior and empower you to make data-driven decisions during battery system verification and validation.
Conclusion
Typhoon HIL’s BMS HIL Testbed revolutionizes BMS development and testing, by providing a comprehensive, high-precision solution that reduces risks, accelerates development cycles, and ensures robust system performance. With detailed, scalable, and safe testing capabilities, Typhoon HIL empowers you to drive innovation and lead the charge for next-generation BMS solutions.