Machine settings
This section describes machine settings
The Machine settings is divided into 2 parts:
- Load settings
- Initialization settings
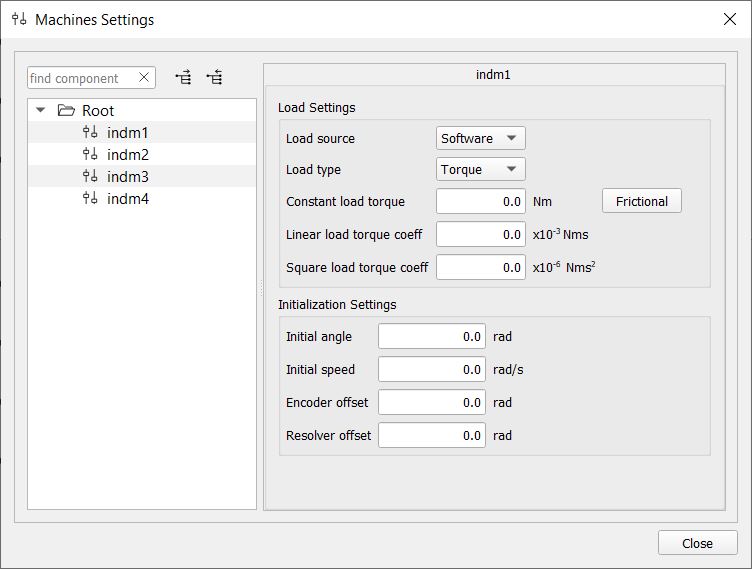
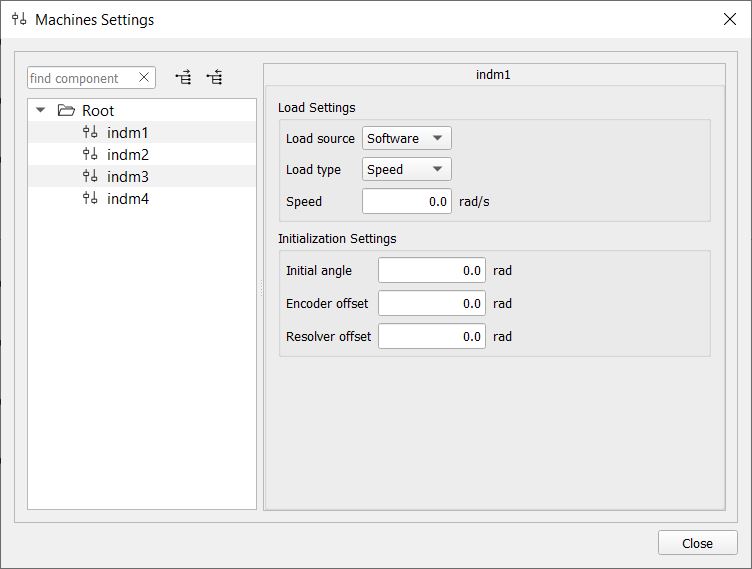
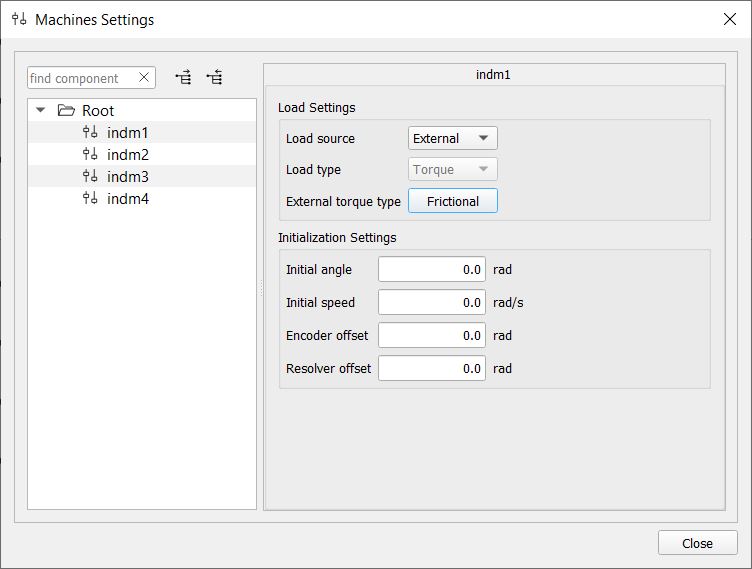
Load settings for a machine include the following:
- Load source - defines the machine load source and has two states: 'Software' and 'External'. In the 'Software' state, the load is defined by load components from the GUI machine pane. In the 'External' state, the load is controlled externally from the model-defined analog input pin. By default, the torque source is set to 'Software'.
- Load type –defines the type of machine load. It can be 'Torque' or 'Speed'. Some of the settings will not be available when the Speed load type is selected (Figure 1 and Figure 2).
- Speed – sets the machine speed in rad/s. This setting will only be visible when the ‘Speed’ load type is selected. When setting the speed value, please note that the upper limit of emulated speed on all HIL devices is 20,000 rad/s. If the speed exceeds this value, an arithmetic overflow flag will occur.
- External torque type – sets the external torque type of a machine. It can be ‘Frictional’ and ‘Potential’. This setting will only be visible when the 'External' torque source is selected.
- Const load torque – defines the constant load torque and is set in absolute units (Nm). When the potential load type is selected, attention must be paid to the upper limit of this torque. If the load torque exceeds the motor torque, the rotor speed rapidly increases in the opposite direction until the calculation limit indicated by the arithmetic overflow flag is reached. This can be prevented by applying appropriate values of linear and/or square load torque.
- Const load type button – defines the constant load type. 'Frictional' load type always opposes the machine rotation, while the 'Potential' type has a defined torque sign and does not depend on the direction of rotation.
- Linear load torque coeff – this is a coefficient that multiplies the rotor mechanical speed. Consequently, it is given in (Nms) units. The linear load torque always opposes the machine rotation. Therefore, for values above a certain limit, it would force the rotor to stop.
- Square load torque coeff – this is a coefficient that multiplies the squared rotor mechanical speed. Consequently, it is given in (Nms^2) units. The square load torque always opposes the machine rotation. Therefore, for values above a certain limit, it would force the rotor to stop.
Initialization settings for a machine include the following:
- Initial angle – defines the initial mechanical angle of the machine.
- Initial speed – defines the initial mechanical angular speed of the machine.
- Incremental encoder offset – defines the angle between the mechanical zero angle of the machine and the zero-marker position of the incremental encoder.
- Sine encoder/resolver offset - defines the angle between the mechanical zero angle of the machine and the sine encoder and the resolver zero angle.
Note: Spin-box update policy - new values of all spin-box components are sent to the
HIL device by pressing the Enter key on the keyboard. Values that are not sent to the HIL
device are marked with a red background.