Three Phase Two Winding Variable Ratio Transformer
Description of the Three Phase Two Winding Variable Ratio Transformer component in Schematic Editor
Component description
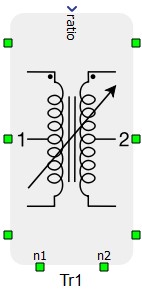
Three Phase Two Winding Variable Ratio Transformer is modeled as three single phase variable ratio transformers, meaning that only magnetic coupling between windings of the same phase are taken into account.
The magnetization inductance Lm can be modeled as linear or with saturation. Core losses are modeled as a shunt resistance Rm. Both Lm and Rm are modeled on the primary side of the transformer. It is possible to neglect Lm and Rm by selecting Lm/Rm neglected in the Core model property. For more information on the core model, please refer to Core model.
When the Core model property is set to Lm/Rm neglected, the primary inductance L1 may be degenerated. If it is desired to preserve L1, a snubber can be defined under the stability tab to provide an alternative current path at the transformer primary. Alternatively, the Refer L1 to secondary checkbox provides the option to refer the effects of inductance L1 to the secondary side of the transformer. If this option is selected, inductances L1 and L2 are replaced with a single variable inductor L2_var on the transformer secondary.
The ratio input is used ot set the turns ratios of each of the three internal transformers. The input can either be a single value or an array. If a one-dimensional input is provided, the given ratio will be assigned to each transformer. If an array is provided, the entries in index positions 0, 1, and 2 will be assigned to phases A, B, and C respectively.
It should be noted that terminals N1 and N2 can be connected with the rest of the circuit in Schematic Editor only if the corresponding side is wye (Y) connected.
The topology of the Three Phase Two Winding Variable Ratio Transformer is designed to match that of the Three Phase Two Winding Transformer. A schematic block diagram of the Three Phase Two Winding Variable Ratio Transformer with corresponding component arrangement and naming is shown in Figure 2.
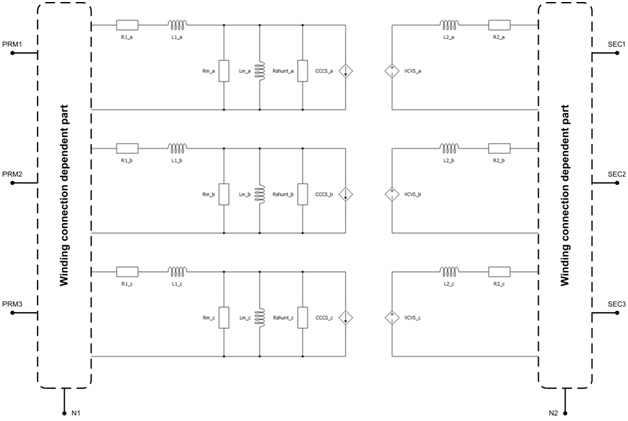
There are two types of tests that are performed to characterize a transformer. Both of the tests are performed on either the primary or the secondary side of the transformer. The tests are:
- short circuit test – exciting a set of three-phase windings while the other set of windings is short circuited
- open circuit test – exciting a set of three-phase windings while the other set of windings is open circuited
Measurement results obtained from these tests and other information given on the transformer’s nameplate provide the necessary data for transformer characterization and modeling.
Winding excitation in the tests is the three-phase positive sequence voltage. In addition to that, when characterizing a transformer and making a transformer model that includes mutual inductances between phases, it is necessary to perform the same tests, but with excitation being the three-phase zero sequence voltage.
Parameters of the equivalent circuit are calculated as follows. During the short circuit test, the magnetization branch is considered shorted by the short circuited winding. So, the primary side short circuit impedance is obtained by:
The primary side short circuit resistance is obtained by:
The primary side short circuit inductance is obtained by:
The primary and secondary side resistances and short circuit inductances are calculated using:
From the positive sequence open circuit test results, it is obtained:
Variables description:
Sn - nominal power of transformer
V1nph - primary side nominal phase to phase voltage
fn - nominal frequency
N2/N1 - transfer ration
uscd - short circuit voltage (sc) – positive sequence (d)
Zscd - short circuit impedance (sc) – positive sequence (d)
Pscd - short circuit active power (sc) – positive sequence (d)
Rsc - short circuit resistance (sc)
Lscd - short circuit inductance (sc) – positive sequence (d)
R1 - resistance on primary side
R2 - resistance on secondary side
L1d - leakage inductance on primary side – positive sequence (d)
L2d - leakage inductance on secondary side – positive sequence (d)
iocd - open circuit (oc) excitation current – positive sequence (d)
i1nph - nominal phase current
Pocd - open circuit (oc) losses– positive sequence (d)
RFed (Rm) - resistance representing the core losses under nominal voltage – positive sequence (d)
iFed - current due to core losses under nominal voltage – positive sequence (d)
imd - magnetizing current – positive sequence (d)
Lmd - magnetizing inductance – positive sequence (d)
Ports
- prm_1 (electrical)
- Primary winding phase 1 port 1.
- prm_1_2 (electrical)
- Available if Winding 1 connection is set to O.
- Primary winding phase 1 port 2.
- prm_2 (electrical)
- Primary winding phase 2 port.
- prm_2_1 (electrical)
- Available if Winding 1 connection is set to O.
- Primary winding phase 2 port 1.
- prm_2_2 (electrical)
- Available if Winding 1 connection is set to O.
- Primary winding phase 2 port 2.
- prm_3 (electrical)
- Primary winding phase 3 port.
- prm_3_1 (electrical)
- Available if Winding 1 connection is set to O.
- Primary winding phase 3 port 1.
- prm_3_2 (electrical)
- Available if Winding 1 connection is set to O.
- Primary winding phase 3 port 2.
- sec_1 (electrical)
- Secondary winding phase 1 port 1.
- sec_1_2 (electrical)
- Available if Winding 2 connection is set to O.
- Secondary winding phase 1 port 2.
- sec_2 (electrical)
- Secondary winding phase 2 port.
- sec_2_1 (electrical)
- Available if Winding 2 connection is set to O.
- Secondary winding phase 2 port 1.
- sec_2_2 (electrical)
- Available if Winding 2 connection is set to O.
- Secondary winding phase 2 port 2.
- sec_3 (electrical)
- Secondary winding phase 3 port.
- sec_3_1 (electrical)
- Available if Winding 2 connection is set to O.
- Secondary winding phase 3 port 1.
- sec_3_2 (electrical)
- Available if Winding 2 connection is set to O.
- Secondary winding phase 3 port 2.
- n1 (electrical)
- Available if Winding 1 connection is set to Y.
- Primary winding neutral port.
- n2 (electrical)
- Available if Winding 2 connection is set to Y.
- Secondary winding neutral port.
- ratio
- Turns ratios of each of the three internal transformers.
- out
- Available if Enable signal output option is checked.
- Primary and secondary voltage and current values for the individual single phase transformers. Each of the output signals is instantaneous by default. If the Use RMS option is checked, the RMS value of each signal will be applied to port instead.
General (Tab)
- Input parameters
- Specifies parameters format (pu, SI, SC and OC tests).
- Sn
- Available if Input parameters is set to pu or SC and OC tests.
- Nominal Power of the transformer [VA].
- f
- Available if Input parameters is set to pu or SC and OC tests.
- Nominal frequency [Hz].
- V1
- Rated line to line voltage of primary winding [Vrms].
- V2
- Rated line to line voltage of secondary winding [Vrms].
- R1
- Available if Input parameters is set to SI.
- Resistance of winding 1 (primary) [Ω].
- r1
- Available if Input parameters is set to pu.
- Resistance of winding 1 (primary) [p.u.].
- L1
- Available if Input parameters is set to SI.
- Leakage inductance of winding 1 (primary) [H].
- l1
- Available if Input parameters is set to pu.
- Leakage inductance of winding 1 (primary) [pu].
- R2
- Available if Input parameters is set to SI.
- Resistance of winding 2 [Ω].
- r2
- Available if Input parameters is set to pu.
- Resistance of winding 2 [pu].
- L2
- Available if Input parameters is set to SI.
- Leakage inductance of winding 2 [H].
- l2
- Available if Input parameters is set to pu.
- Leakage inductance of winding 2 [pu].
- usc1
- Available if Input parameters is set to SC and OC tests.
- Positive sequence short circuit voltage [% of nominal phase voltage].
- Psc1
- Available if Input parameters is set to SC and OC tests.
- Positive sequence short circuit losses [W].
- Core model
- Selects transformer core model implementation.
- Several levels of model fidelity are available - Linear, Non-Linear or Rm/Lm neglected.
- Rm
- Available if Input parameters is set to SI and Core model is set to Linear or Non-Linear.
- Resistance representing core losses [Ω].
- rm
- Available if Input parameters is set to pu and Core model is set to Linear or Non-Linear.
- Resistance representing core losses [pu].
- Lm
- Available if Input parameters is set to SI and Core model is set to Linear.
- Magnetization inductance [H].
- lm
- Available if Input parameters is set to pu and Core model is set to Linear.
- Magnetization inductance [pu].
- ioc1
- Available if Input parameters is set to SC and OC tests and Core model is set to Linear or Non-Linear.
- Positive sequence no load excitation current [% of nominal current].
- Poc1
- Available if Input parameters is set to SC and OC tests and Core model is set to Linear or Non-Linear.
- Positive sequence no load losses [W].
- Flux values
- Available if Core model is set to Non-Linear.
- List of magnetic flux values [Wb] or [pu].
- Current values
- Available if Core model is set to Non-Linear.
- List of current values [A] or [pu].
- Refer L1 to secondary
- Available if Core model is set to Lm/Rm neglected.
- Refers the effects of inductance L1 to the secondary side of the transformer.
Winding connection (Tab)
- Winding 1 connection
- Specifies primary winding connection - star (Y), delta (D) or open winding (O).
- Winding 2 connection
- Specifies secondary winding connection - star (Y), delta (D) or open winding (O).
- Clock number
- Available if Winding 1 connection and Winding 2 connection are set to Y or D.
- Determines the phase displacement between voltages of primary and secondary windings.
Signal Processing (Tab)
- Execution rate
- Defines the execution rate of measurement and signal processing components [s].
- Enagle signal ouput
- Passes individual phase voltage and current values to a signal processing output port.
- CPU core
- Sets the CPU marker's value for output signals the sub-circuit.
- Use RMS
- Available if Enable signal output option is checked.
- Passes RMS values for measured voltages and currents.
Stability (Tab)
- Snubber Type
- Type of a snubber to add to the current source side of the embedded single phase transformers - None, R or RC.
- Resistance
- Available if Snubber Type is set to R or RC.
- Resistance of the added snubber [Ω].
- Capacitance
- Available if Snubber Type is set to RC.
- Capacitance of the added snubber [F].