Round
Description of the Round component in Schematic Editor, which outputs an input value rounded by one of the chosen methods.
Component icon

Description
The round component outputs a rounded input value using one of the chosen methods.
Rounding methods can be:
- Floor: Rounds the input signal to its next lower integer, in the -infinity direction.
- Ceil: Rounds the input signal to the next higher integer, in the +infinity direction.
- Round: Rounds the input signal to the closest integer.
- Fixed: Rounds the input signal to the next integer closest to zero, that is, it chops off the fractional part of the input signal. In other words, the input signal is rounded up for negative numbers and rounded down for positive numbers.
The the table below illustrates some examples with the functionality of each round method:
| in | round method | out |
| 1.4 | floor | 1 |
| 1.4 | ceil | 2 |
| 1.4 | round | 1 |
| 1.4 | fixed | 1 |
| -2.9 | floor | -3 |
| -2.9 | ceil | -2 |
| -2.9 | round | -3 |
| -2.9 | fixed | -2 |
Ports
- Input (in)
- Signal to be rounded.
- Supported types: uint, int and real.
- Vector support: yes.
- Signal to be rounded.
- Output (out)
- Rounded signal.
- Supported types: uint, int and real.
- The output type is inherited from the input signal.
- Vector support: yes.
- The vector length is inherited from the input signal.
- Supported types: uint, int and real.
- Rounded signal.
Properties
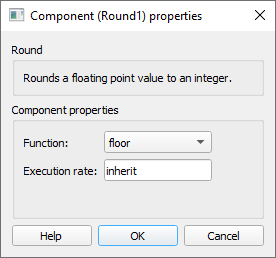
- Round function
- Select the rounding method that will be applied to the input signal. The method can be floor, ceil, round or fixed.
- Execution rate
- Type in the desired signal processing execution rate. This value must be compatible with other signal processing components of the same circuit: the value must be a multiple of the fastest execution rate in the circuit. There can be up to four different execution rates. To specify the execution rate, you can use either decimal (e.g. 0.001) or exponential values (e.g. 1e-3) in seconds. Alternatively, you can type in ‘inherit’ in which case the component will be assigned execution rate based on the execution rate of the components it is receiving input from.