Start event trigger
Overview of the ways to start event trigger.
Start event trigger via the API
from tth.client import APIKeyClient
hub_address = "https://tth-address.cloud"
api_key_value = "apiKeyValue"
trigger_id = 1
trigger_parameters = {"parameter_name": "parameter_value"}
# create API Key client
client = APIKeyClient(hub_address, api_key_value)
# start event trigger
execution_id = client.trigger.start(trigger_id, trigger_parameters)
# obtain details of started execution
execution_info = client.execution.get_info(execution_id)
print(execution_info)
# obtain execution status
execution_status = client.execution.get_status(execution_id)
print(execution_status)
# wait for execution to finish
execution_status = client.execution.wait_until_finished(execution_id)
print(execution_status)
import requests
auth_token = 123456 # Replace with the token value of the trigger you want to start
tth_url = "URL" # Replace URL with the URL of your TTH
trigger_id = 4 # Replace with the Trigger Number you would like to start
branch = "main"
trigger_url = f"{tth_url}/api/triggers/start/{trigger_id}"
exec_id = requests.post(trigger_url, headers={'X-API-Key': auth_token}).json()
exec_url = f"{tth_url}/api/executions/status/{exec_id}"
while True:
exec_status = requests.get(exec_url,
headers={'X-API-Key': auth_token},
json={"parameters": [{"name": "BRANCH", "value": branch}]}).json()['status']
if exec_status not in ['QUEUED', 'RUNNING']
break
if exec_status != 'PASSED':
raise Exception("HIL Job did not pass!")
Start event trigger with the webhook
Popular source code management platforms such as GitLab and GitHub provide webhooks - mechanism to start jobs on other platforms. A webhook is a way for one system to send real-time data to another system as soon as some event happens. In case of the source code management platforms, event can be pushing new code to a branch or merging a branch to some other branch. When such event happens, request can be sent to Typhoon Test Hub to start an event trigger. Although some platforms such as GitLab allow defining custom request bodies (and sometimes request headers) when requests are sent via webhook, most platforms like GitHub and BitBucket always send data according to fixed schemas.
- Insert proper URL that corresponds to the URL of the event trigger that you would like to be started from the webhook
- Insert API key value as the secret token
- Check if data is sent in JSON format
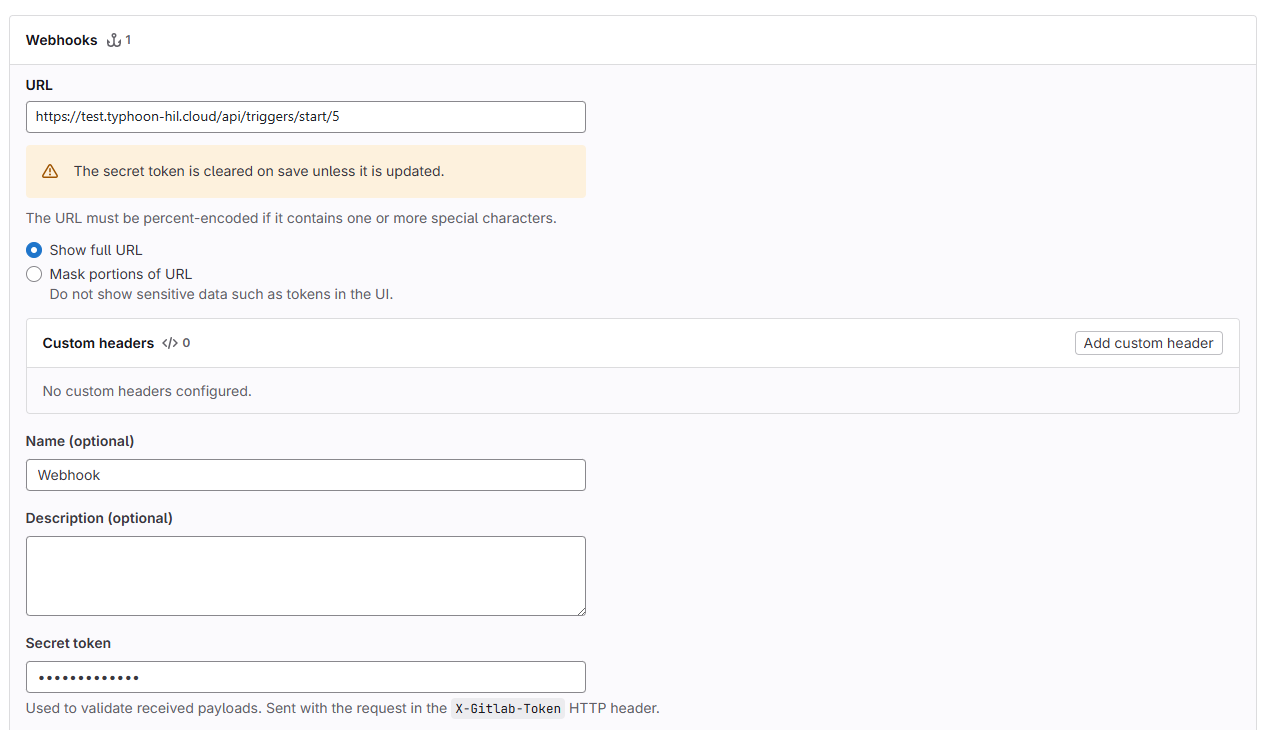
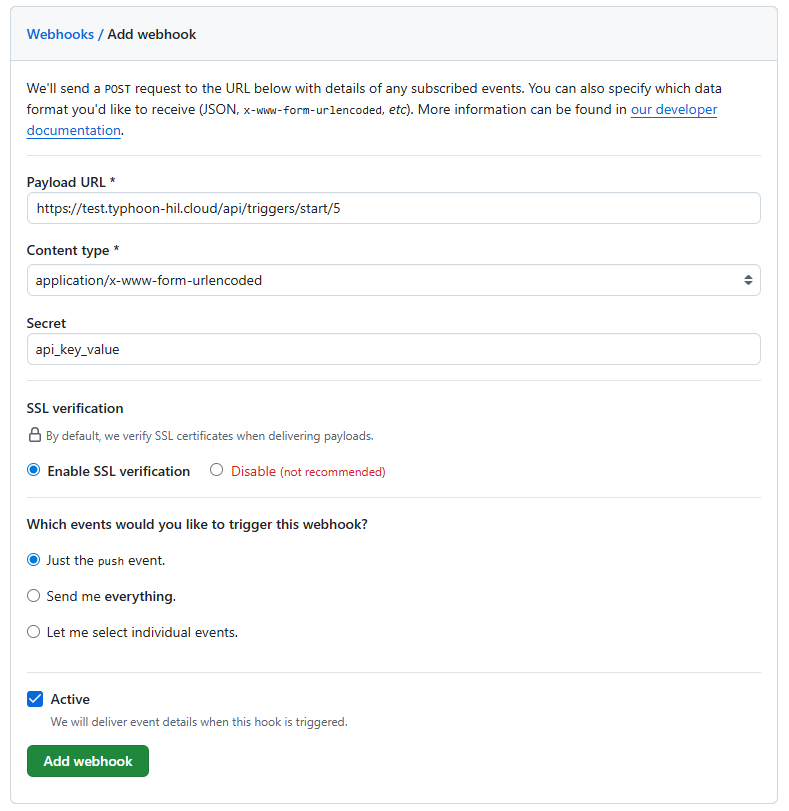
https://test.typhoon-hil.cloud/api/triggers/start/5?first_param=first_value&second_param=second_value
{
"ref": "ref/heads/develop",
"repository: {
"url": "https://test.gitlab.com/my/repository",
"description": "repository description"
}
}